By: CS2103-AY1819S2-W10-1 Since: Jan 2019 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. How To Use This Guide
- 3. Quick Start
- 4. Features
- 5. Contexts
- 6. Commands
- 6.1. Command Format
- 6.2. Non-contextual commands
- 6.2.1. Custom user command macro:
macro[coming in v2.0] - 6.2.2. Export settings and data to an export file :
export[coming in v2.0] - 6.2.3. Import settings and data from an export file :
import[coming in v2.0] - 6.2.4. Adding a single entry:
add - 6.2.5. Subscribing to a feed:
subscribe - 6.2.6. Listing entered commands :
history - 6.2.7. Enabling or disabling offline mode :
offline - 6.2.8. Viewing help :
help - 6.2.9. Exiting the program :
exit
- 6.2.1. Custom user command macro:
- 6.3. Context-switching commands
- 6.3.1. Showing your Reading List:
list - 6.3.2. Showing your Archives:
archives - 6.3.3. Searching the web:
bing - 6.3.4. Searching for news:
googlenews - 6.3.5. Previewing a web feed:
feed - 6.3.6. Searching a web page for links:
links[coming in v2.0] - 6.3.7. Showing feeds:
feeds - 6.3.8. Searching online for feeds:
searchfeeds[coming in v2.0] - 6.3.9. Showing reading statistics:
stats[coming in v2.0]
- 6.3.1. Showing your Reading List:
- 6.4.
Reading ListContext Commands- 6.4.1. Editing an entry:
edit - 6.4.2. Finding entries (by title, description, etc.):
find - 6.4.3. Selecting an entry:
select - 6.4.4. Changing the view mode:
view - 6.4.5. Refreshing an entry:
refresh - 6.4.6. Refreshing all displayed entries:
refreshall - 6.4.7. Marking an entry as read:
read[coming in v2.0] - 6.4.8. Marking an entry as unread:
unread[coming in v2.0] - 6.4.9. Sharing an entry:
share[coming in v2.0] - 6.4.10. Archiving an entry:
archive - 6.4.11. Archiving all displayed entries:
archiveall - 6.4.12. Deleting an entry:
delete - 6.4.13. Deleting all displayed entries:
deleteall - 6.4.14. Clearing all entries :
clear
- 6.4.1. Editing an entry:
- 6.5.
ArchivesContext Commands - 6.6.
Search ResultsContext Commands - 6.7.
FeedsContext Commands - 6.8.
Feeds SearchContext Commands[coming in v2.0]
- 7. FAQ
- 8. Command Summary
1. Introduction
README is an integrated bookmark manager and feed reader desktop application that helps you read more content you care about anywhere you go.
You’ll love README if you consume a lot of web content and want to keep up to date with your favourite websites but you’re a road warrior who doesn’t have regular Internet access.
Whether you’re heading off on a long flight or working in a cafe, README has you covered with all the content you care about in one place.
README is for those who prefer to use a desktop app for subscribing to web feeds and saving web pages to read later on their personal computer.
More importantly, README is optimized for those who prefer to work with a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI).
If you can type fast, README can make you more efficient at consuming content than traditional GUI apps.
Jump to Section 3, “Quick Start” to get started!
2. How To Use This Guide
This User Guide contains everything you need to know in order to use README. You don’t need to read this Guide from start to finish - it is designed to help you find exactly what you need.
See Section 3, “Quick Start” to get up and running quickly.
See Section 4, “Features” to learn about how README works.
See Section 6, “Commands” to find out what each command does and the parameters you need to supply.
Here are icons we use and what they mean:
| Useful but non-crucial information. |
| Helpful information that may make your experience better. |
| Important information about potential issues that may occur. |
3. Quick Start
Get started quickly by installing README, getting to know its user interface, and touring of its main features!
3.1. Installation
-
Ensure you have Java version
9or later installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
README.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your README.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
3.2. User Interface
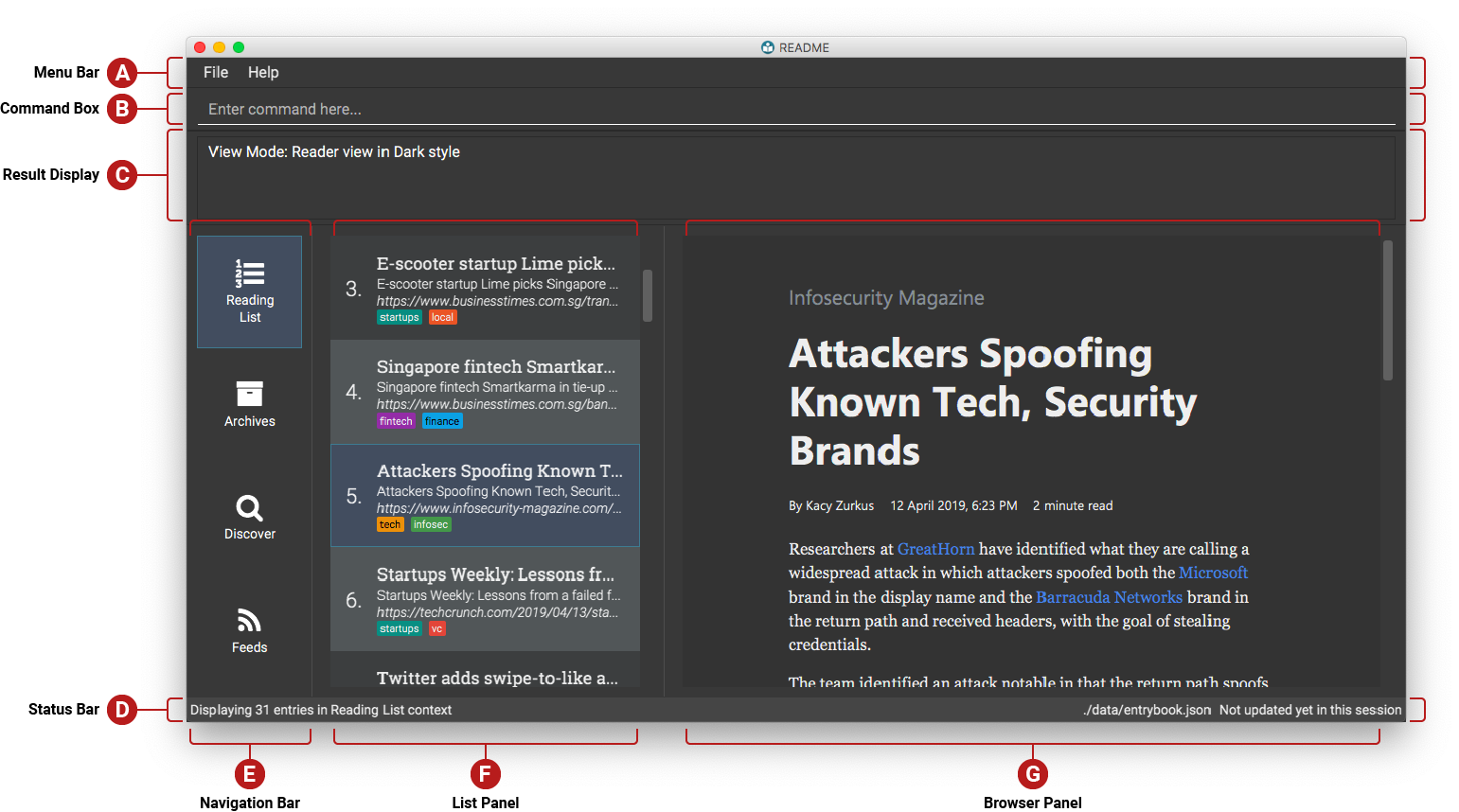
This is how the application should look like!
Enter your commands in the Command Box (B), and the execution result message will appear in the Result Display (C).
Browse your saved entries from the List Panel (F), and select any one of them to view it in the Browser Panel (G).
3.3. Quick Tour of Basic Features
-
Type the command in the Command Box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Try these commands in order!
-
list: shows your reading list of saved links -
addl/https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special:Random: adds a random Wikipedia page to your reading list -
select1: selects the Wikipedia page for reading -
addl/https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Main_Page: adds the Wikipedia main page to your reading list -
googlenews: displays the current top stories from Google News -
add1: adds the first news article to your reading list -
list: goes back to your reading list -
select3: selects the just-added news article for reading -
viewreader: switches to a more comfortable reading experience -
archive3: archives the news article -
archives: shows your archived links -
delete1: delete the archived news article -
feeds: shows your subscribed feeds -
subscribel/https://www.buzzfeed.com/index.xml ti/BuzzFeed: subscribes to the BuzzFeed news feed (this can take a while) -
list: goes back to your reading list -
refresh1: refreshes the first entry to get most recent version from internet -
select1: views the updated entry -
exit: exits the app
-
-
Refer to Section 6, “Commands” for details of each command.
4. Features
4.1. Overview
4.1.1. Link Saving and Management - Read Anything
README helps you capture the content that you discover online.
Save the latest news stories, magazine articles, recipes, how-tos – anything you discover online. Whenever you find a web page you want to read later, add it to your reading list in README. To help you organize the mountain of content, README lets you tag link so you can always find what you’re looking for, and archive or delete links you’ve finished reading so your reading list won’t become cluttered.
4.1.2. Web Feeds Subscription - Read More
README keeps you up to date with your favourite websites.
Integrations with Bing Web Search and Google News mean you’ll never run out of things to read. Search for particular topics you’d like to know more about or just read the top news stories - it’s up to you. As README also functions as a feed reader, you can subscribe and unsubscribe from any RSS or Atom feed available on the Internet. Whenever you open README, the latest content from your subscribed feeds is automatically added to your reading list.
4.1.3. Offline Support - Read Anywhere
README lets you read offline, even on airplanes, trains, or on Wi-Fi-only devices away from Internet connections.
Whenever you save a link, README automatically downloads its web page to your personal computer if there is an Internet connection. This gives you the convenience of viewing your saved links anywhere, anytime, even if there is no Internet connection. If you still want to keep a link but no longer need to view it offline, you can archive it. This will delete its downloaded web page from your personal computer.
4.1.4. Reader View - Read Better
README makes your long reading sessions so much more comfortable.
Reader View strips out all the visual clutter from web pages and presents content in a perfectly formatted, clean layout, so you can focus on the content without any unnecessary distractions. You can even choose the colour scheme that suits you best - try the white or sepia style if you’re reading in a lighted environment, or the dark or black styles in a dark environment.
4.2. Glossary
4.2.1. Common Terms
-
Feed
A data format used by content providers to provide users with frequently updated content. Also known as a web feed, they can be found all over the web - you can usually find a link to them titled "RSS feed" or "Atom feed" at the footer of a website. -
Link
Short for "hyperlink", a reference to a URL you can follow by clicking on its text. -
Tag
A label attached to an entry for the purpose of identification or to give other information. -
URL
An address to a web resource, usually beginning withhttp://orhttps://. Stands for Uniform Resource Locator.
4.2.2. README-specific Terms
-
Command
An instruction you type in that makes README perform a function. -
Entry
The name we use for a single web page that has been added to README. Similar to a bookmark, comprising URL, Title, and Description fields among others. -
Context
The Context determines which Entries are displayed and what Commands are available. The four contexts are Reading List, Archives, Search Results and Feeds. Refer to Section 5, “Contexts” for more information. -
Reading List
When you or a web feed that you Subscribe to Adds a new Entry, it is saved to your Reading List. Entries in your Reading List have their web pages automatically downloaded onto your personal computer for offline viewing. When you’re finished with an Entry, you can move it to your Archives for safekeeping. -
Archives
When you’re finished with an Entry but would like to keep it for future reference, you can move it to the Archives. Archived items will still be available for viewing but will not have their web pages automatically downloaded to your personal computer. Therefore, you’ll need an Internet connection to view Entries in your Archives. -
Search Results
When you Search online for new Entries, they are temporarily stored here until you do another Search. You can Add an Entry from here to your Reading List. -
Feeds
Feeds you Subscribe to are listed here. You can Subscribe to a new Feed or Unsubscribe from an existing one. -
Add
The action of adding a web page as an Entry to your Reading List. Sometimes we may refer to this as Saving as well. -
Edit
If you would like to change the URL, Title, or Description fields or Tags of an Entry, you can Edit it. -
Archive
If you’re finished with an Entry but would like to keep it for future reference, you can Archive it. This will move the Entry from your Reading List to your Archives. Archived Entries can be Unarchived. -
Unarchive
If you’ve Archived an Entry but would like its web page to be downloaded to your personal computer, you can Unarchive it. This will move the Entry from your Archives to your Reading List. Unarchived Entries can be Archived again. -
Delete
If you do not wish to keep an Entry, you can Delete it. This will permanently remove an Entry. Deleted Entries cannot be recovered. -
Find
The action of finding certain existing Entries. You can narrow down to those that contain certain keywords. -
Select
If you would like to view an Entry’s web page, you can Select it. You can also choose a View Mode. -
View Mode
The View Mode determines how an Entry’s web page is displayed. The two available View Modes are Reader View and Browser View. -
Reader View
Reader View displays a web page in a simplified layout that makes reading enjoyable and free of distracting ads, fancy layouts, and other extraneous things. You can customize the colour scheme to meet your own preferences. -
Browser View
Browser View displays a web page just as it would appear in its original form in your web browser. -
Search
The action of searching online for new Entries to Add. You can use Bing Web Search or Google News Search. -
Subscribe (to a website’s Feed)
Keep up to date with a website by having any new Entries added to your Reading List. -
Unsubscribe (from a website’s Feed)
Stop adding any new Entries from the website to your Reading List.
5. Contexts
README supports many features, from bookmarking and archiving to subscribing to feeds and searching for new content.
To help you navigate these features, we divided these functions into four major partitions, or contexts:
-
Reading List
-
Archives
-
Search Result
-
Feeds
Navigate the contexts via our context-switching commands (see Section 6.3, “Context-switching commands”), or by clicking the buttons on the sidebar!
The Discover button brings you to the Search Result context!
|
For more information on what commands and functions are available in each context, refer to the section below!
6. Commands
6.1. Command Format
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters you need to supply.-
For example, in
add l/URL,URLis a parameter which can be used asadd l/https://nus-cs2103-ay1819s2.github.io/cs2103-website.
-
-
Parameters in square brackets are optional.
-
For example,
l/URL [ti/TITLE]can be used asl/https://nus-cs2103-ay1819s2.github.io/cs2103-website/ ti/CS2103 Websiteor asl/https://nus-cs2103-ay1819s2.github.io/cs2103-website/.
-
-
Parameters with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.-
For example,
[t/TAG]…can be used ast/tech,t/tech t/businessetc.
-
-
Parameters can be in any order.
-
For example, if a command specifies
ti/TITLE d/DESCRIPTION,d/DESCRIPTION ti/TITLEis also acceptable.
-
6.2. Non-contextual commands
These commands can be used from any context.
6.2.1. Custom user command macro: macro [coming in v2.0]
Creates macros that compose commands together.
Format: macro MACRO_NAME NUM_ARGS command1; command2; … commandN
Examples:
-
Adding a macro to quickly archive all entries with given tags.
-
macro archive-tags-which-are-old 1 find t/$1; archiveall
-
6.2.2. Export settings and data to an export file : export [coming in v2.0]
Exports the feeds, saved data, history, and other preferences to an export file.
Format: export FILE_PATH
Examples:
-
Saves an export file to desktop
-
export /home/tt/Desktop
-
-
Saves an export file to desktop
-
export C:\Users\Name\Desktop
-
6.2.3. Import settings and data from an export file : import [coming in v2.0]
Imports the feeds, saved data, history, and other preferences from an export file.
Format: import FILE_PATH
Examples:
-
Saves an export file to desktop
-
import /home/tt/Desktop/export.jtjr
-
-
Saves an export file to desktop
-
import C:\Users\Name\Desktop\export.jtjr
-
6.2.4. Adding a single entry: add
Adds a single entry from a link URL to your reading list. Content is automatically downloaded onto your personal computer.
Format: add l/URL [ti/TITLE_OVERRIDE] [d/DESCRIPTION_OVERRIDE] [t/TAG]…
| The entry’s URL must be unique. Duplicate entries with the same URL will not be added! |
The Title and Description fields are automatically filled if you do not provide them.
|
| A entry can have any number of tags (including 0). |
Examples:
-
Adds a single entry with a description and tagged with “Business”
-
add l/https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2019/03/ford-ceo-jim-hackett-ux-design-thinking/580438/ d/Explains why UX is important t/Business
-
6.2.5. Subscribing to a feed: subscribe
Adds a feed and subscribes to its updates.
All entries in the subscribed feed will be added to the reading list.
Format: subscribe l/URL [ti/TITLE_OVERRIDE] [d/DESCRIPTION_OVERRIDE] [t/TAG]..
|
The |
|
A feed can have any number of tags (including 0). |
Examples:
-
Adds a feed whose name is “Kattis”.
subscribe l/https://open.kattis.com/rss/new-problems t/programming
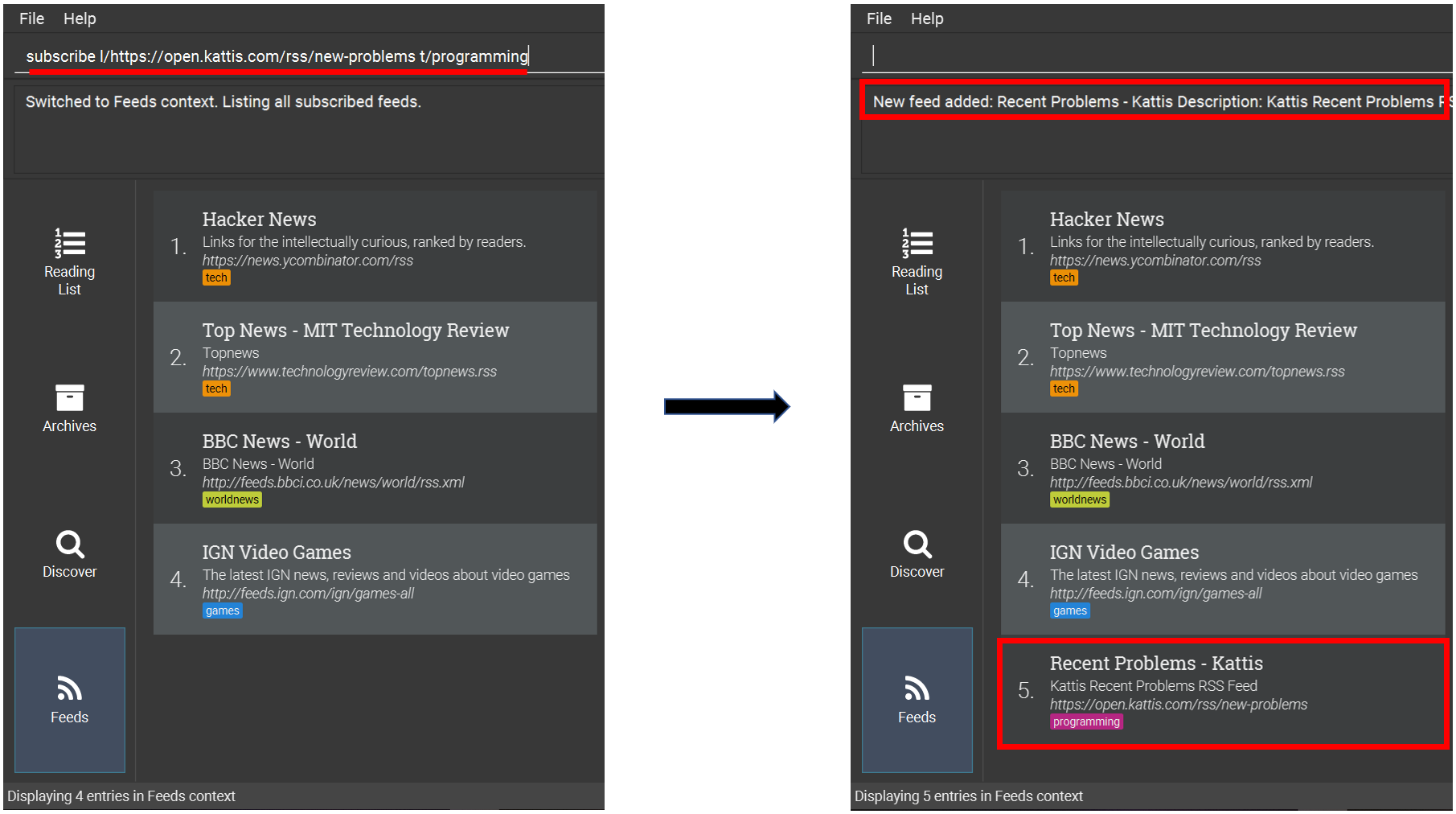
|
The application may be unresponsive for a short while when adding entries from a large feed. |
6.2.6. Listing entered commands : history
Lists all the commands that you have entered in reverse chronological order.
Format: history
|
Pressing the ↑ and ↓ arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box. |
6.2.7. Enabling or disabling offline mode : offline
Some web pages may not work with offline mode.
In order to browse these web pages,
you may temporarily disable offline mode with this command,
or enable it after you wish to re-enter offline mode.
Format: offline MODE(enable, disable)
Examples:
-
Disable offline mode
-
offline disable
-
-
Enable offline mode
-
offline enable
-
|
Offline mode is enabled by default at the start of every session so you don’t have to worry about forgetting to re-enable offline mode |
6.2.8. Viewing help : help
Format: help
6.3. Context-switching commands
These commands can be used from any context but change the context in which only allowed commands are recognised (e.g. archive, unarchive, feed).
6.3.1. Showing your Reading List: list
Shows your Reading List of all saved entries.
This command also enters the Reading List context.
Refer to Section 6.4, “Reading List Context Commands” for available commands in this context.
Format: list
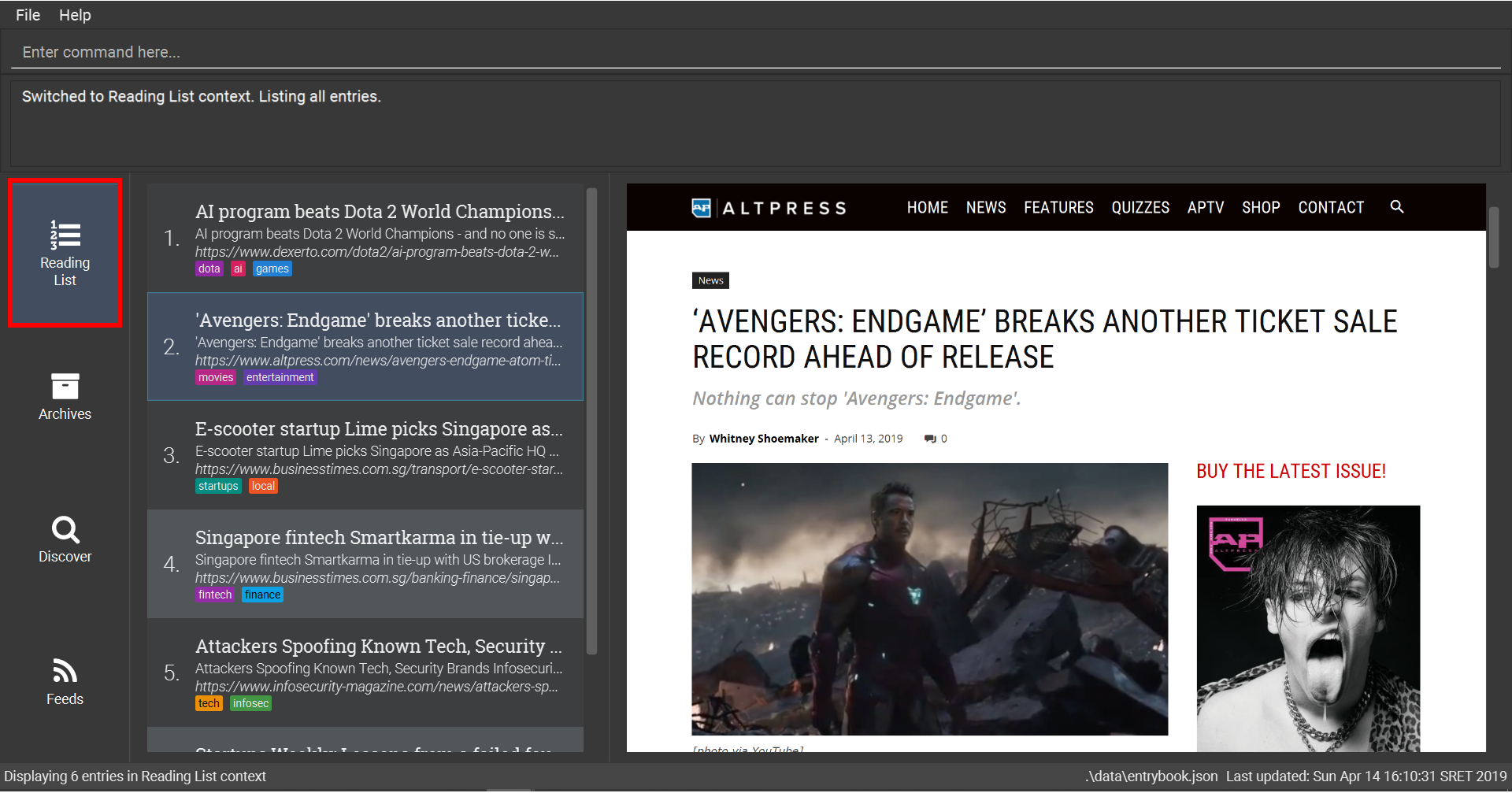
6.3.2. Showing your Archives: archives
Shows your Archives of all archived entries.
This command also enters the Archives context.
Refer to Section 6.5, “Archives Context Commands” for available commands in this context.
Format: archives
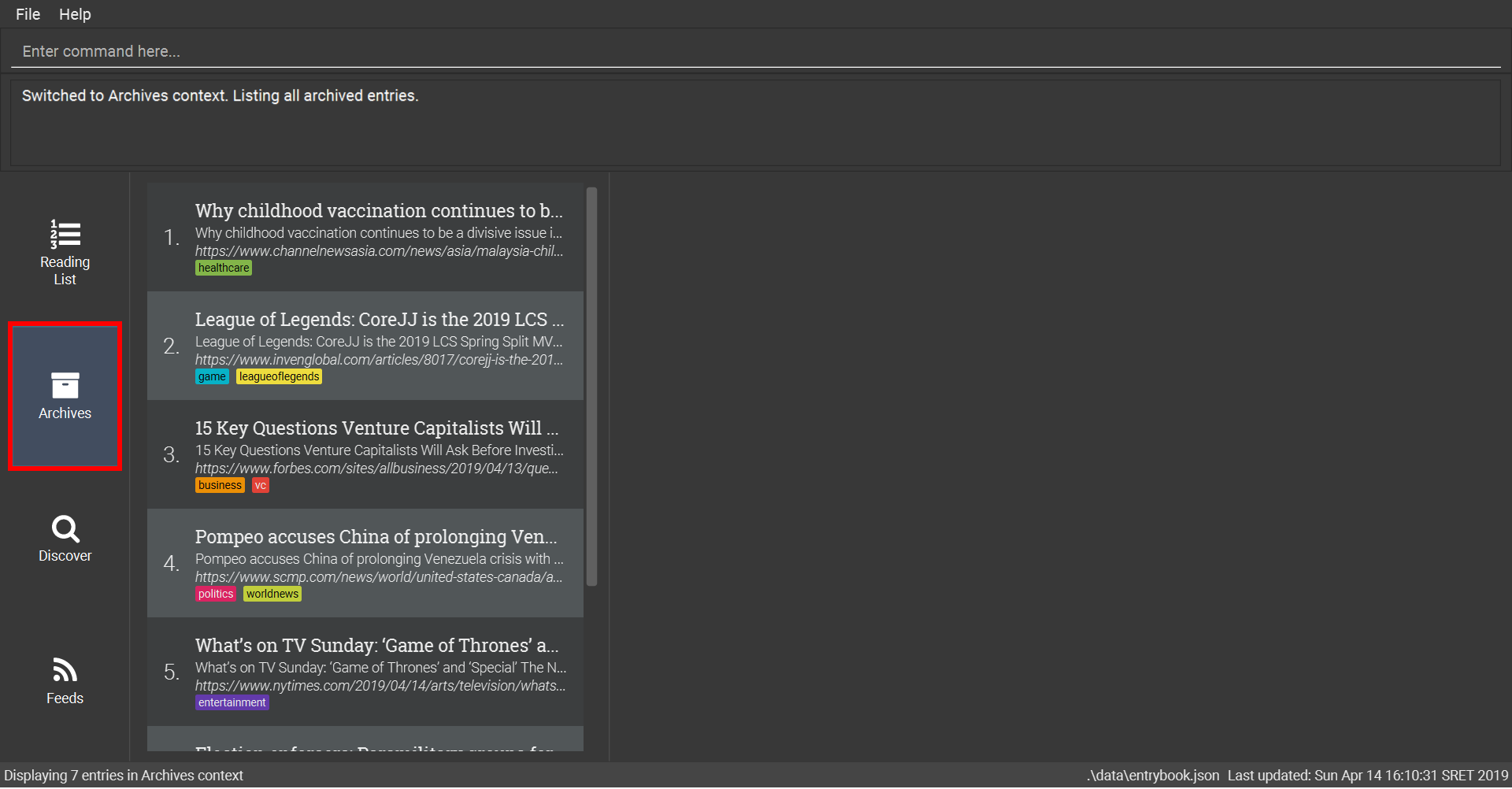
6.3.3. Searching the web: bing
Searches Bing for entries that you can subsequently add.
This command also enters the Search Results context.
Refer to Section 6.6, “Search Results Context Commands” for available commands in this context.
Format: bing [KEYWORD]…
Examples:
-
Bing search the web for entries containing the
Trumpkeyword-
bing Trump
-
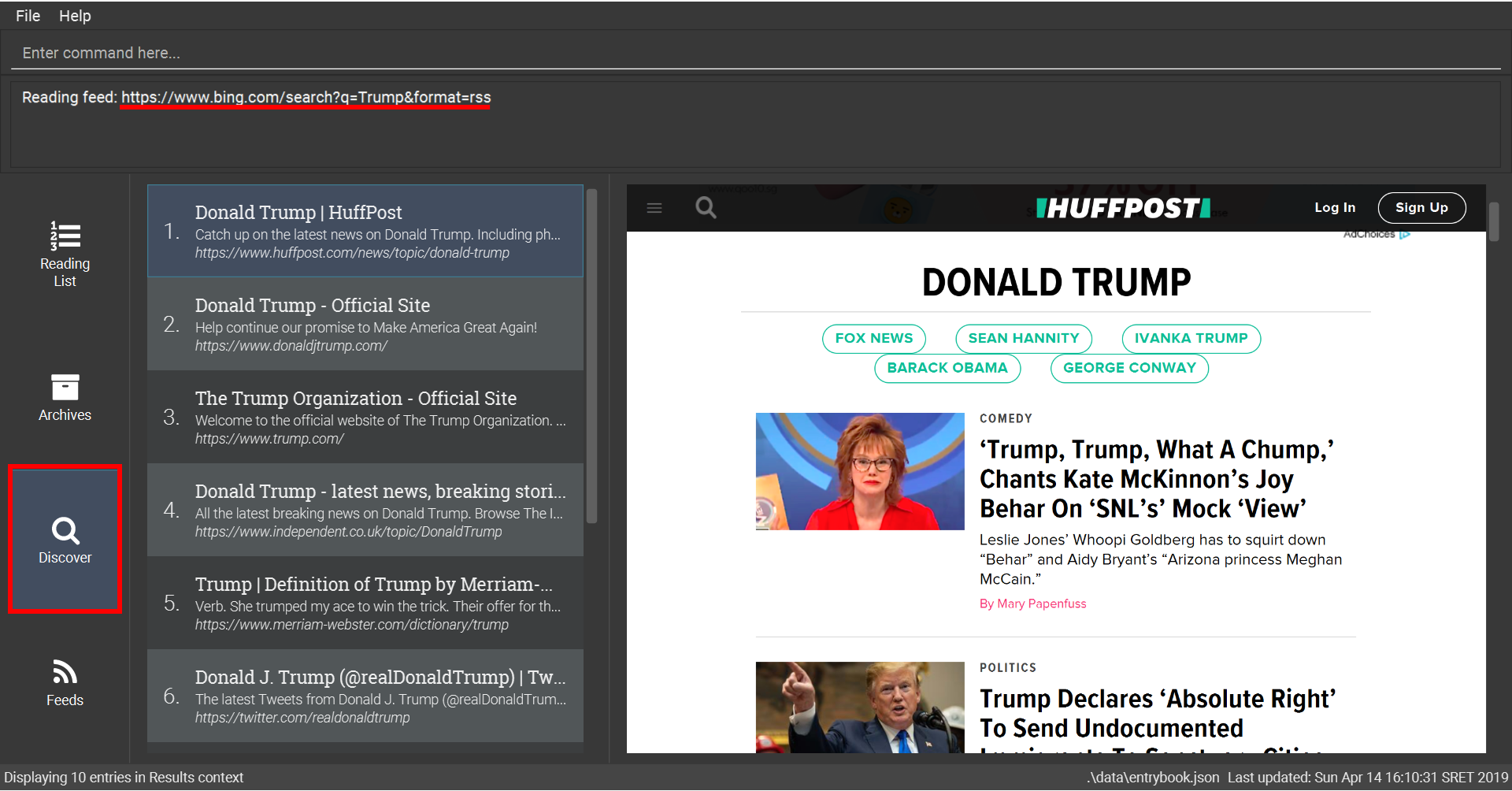
Trump6.3.4. Searching for news: googlenews
Searches Google News for entries that you can subsequently add.
This command also enters the Search Results context.
Refer to Section 6.6, “Search Results Context Commands” for available commands in this context.
Format: googlenews [KEYWORD]…
Examples:
-
View the current top stories on Google News.
-
googlenews
-
-
Search for news articles containing the
Trumpkeyword-
googlenews Trump
-
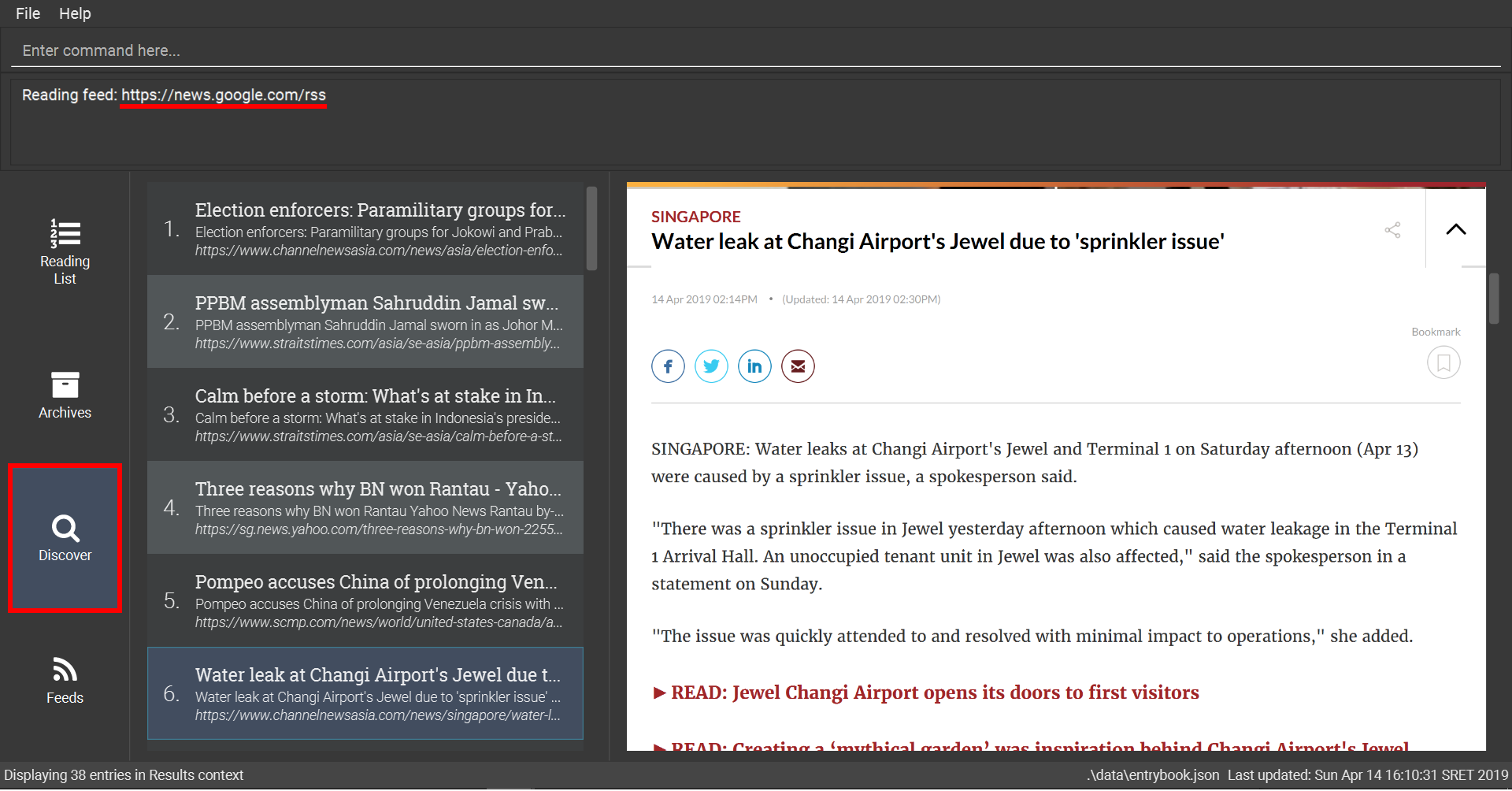
googlenews command6.3.5. Previewing a web feed: feed
Opens a web feed at the URL for previewing.
This command also enters the Search Results context.
Refer to Section 6.6, “Search Results Context Commands” for available commands in this context.
Format: feed [FEED URL]
Examples:
-
Display entries from this feed
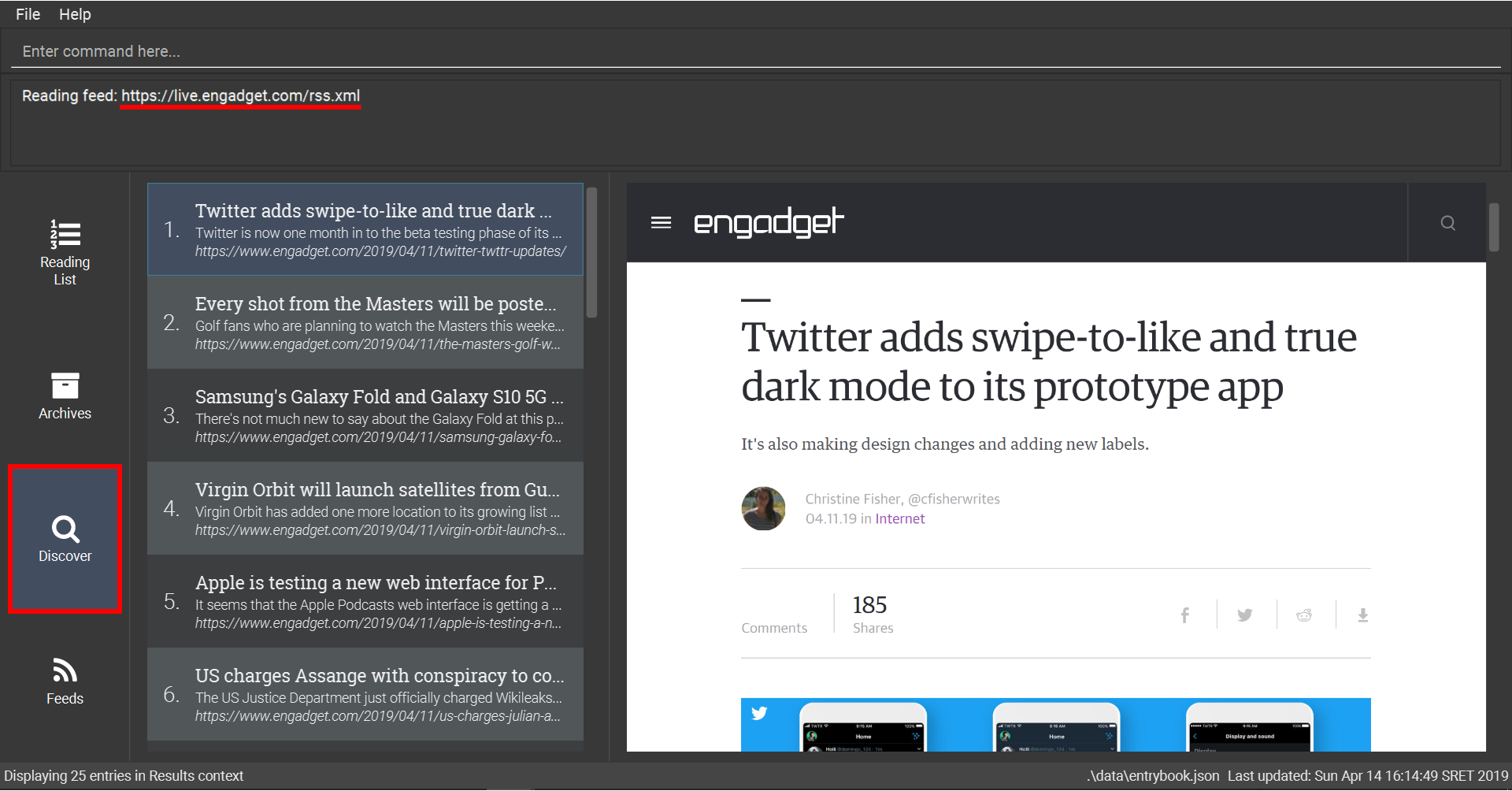
6.3.6. Searching a web page for links: links [coming in v2.0]
Lists all the links in a URL, or the currently displayed web page.
This command also enters the Search Results context.
Refer to Section 6.6, “Search Results Context Commands” for available commands in this context.
Format: links
Format: links [URL]
-
links -
links https://live.engadget.com/2019/02/08/microsoft-internet-explorer-technical-debt/Shows all entries from this article
6.3.7. Showing feeds: feeds
Shows a list of feeds being followed.
This command also enters the Feeds context.
Refer to Section 6.7, “Feeds Context Commands” for available commands in this context.
Format: feeds
Examples:
-
List all feeds
-
feeds
-
-
List all feeds tagged with “Business”
[coming in v2.0]-
feeds t/Business
-
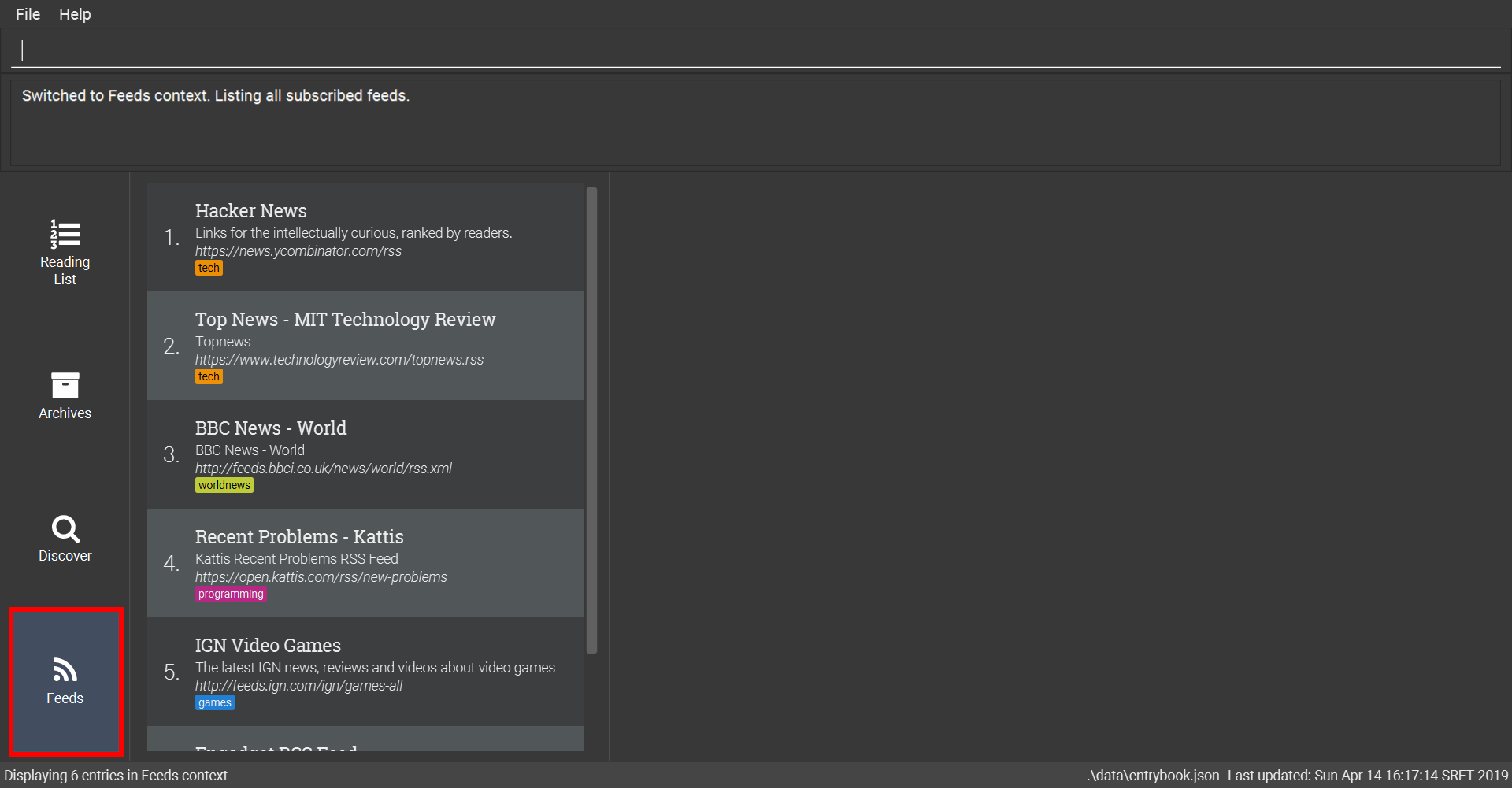
6.3.8. Searching online for feeds: searchfeeds [coming in v2.0]
Searches online for feeds that you can subsequently follow.
This command also enters the Feed Search context.
Refer to Section 6.8, “Feeds Search Context Commands [coming in v2.0]” for available commands in this context.
Format: searchfeeds [KEYWORD]…
Examples:
-
Shows some starter feeds you can add
-
searchfeeds
-
-
Searches for
TechorBusinessfeeds-
searchfeeds Tech Business
-
6.3.9. Showing reading statistics: stats [coming in v2.0]
Shows helpful and fun statistics about your reading progress and habits.
Format: stats
6.4. Reading List Context Commands
To add entries to the reading list, please refer to Section 6.2.4, “Adding a single entry: add”.
6.4.1. Editing an entry: edit
Edits an existing entry in the reading list.
Format: edit INDEX [ti/TITLE_OVERRIDE] [d/DESCRIPTION_OVERRIDE] [r/READ_STATUS] [t/TAG]…
Examples:
-
Edit the title and description of the 1st entry to be
Software Design PatternsandUseful for software engineering project.respectively.-
edit 1 ti/Software Design Patterns d/Useful for software engineering project.
-
-
Clear all existing tags from the 2nd entry.
-
edit 2 t/
-
6.4.2. Finding entries (by title, description, etc.): find
Finds entries whose fields contain any of the given keyphrases.
Format: find [a/SEARCH_PHRASE] [ti/TITLE_SEARCH_PHRASE] [d/DESCRIPTION_SEARCH_PHRASE] [l/LINK_SEARCH_PHRASE] [t/TAG_TO_SEARCH]…
Examples:
-
Find entries with title containing the phrase
lambda, or link containing the phrasegithub.-
find ti/lambda l/github
-
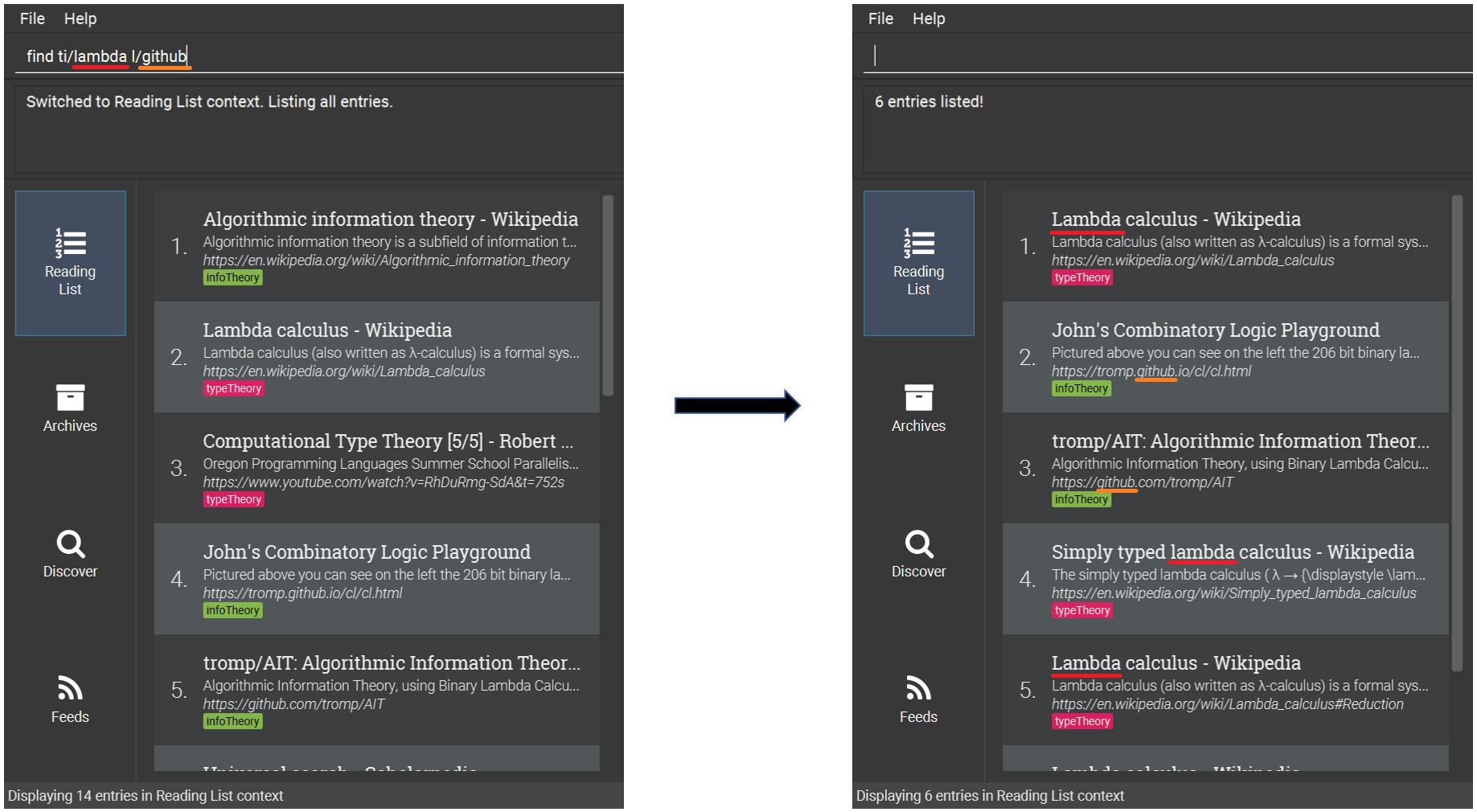
lambda (red) or link containing github (orange) shown after find command-
Find entries with the tag
infoTheory.-
find t/infoTheory
-
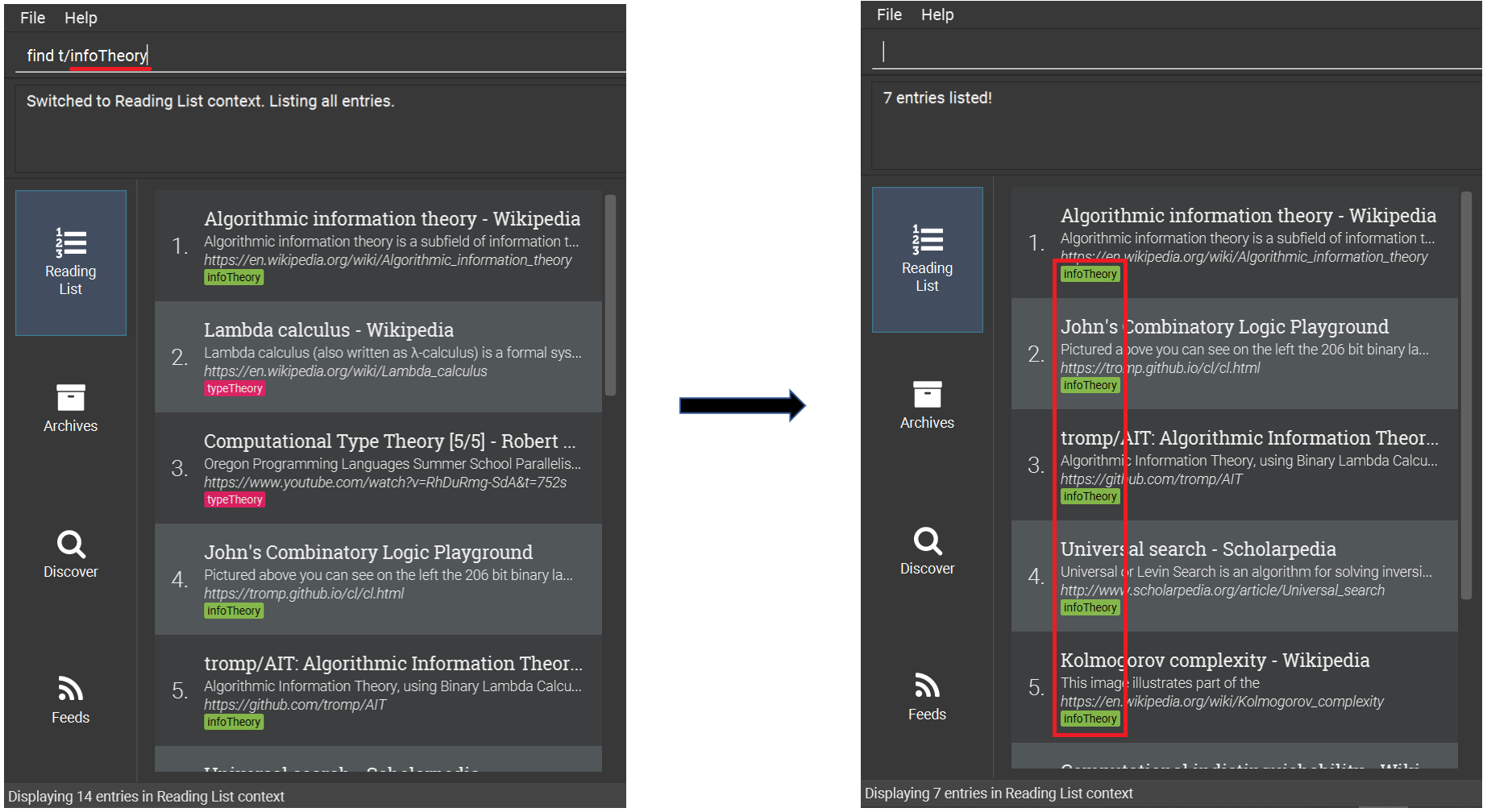
infoTheory shown after find command6.4.3. Selecting an entry: select
Selects the entry identified by the index number used in the displayed entry list for reading.
Format: select INDEX
Examples:
-
Select the 2nd entry in the reading list for reading.
-
list -
select 2
-
-
Select the 1st entry in the find results for the phrase
Trumpin the title.-
find ti/Trump -
select 1
-
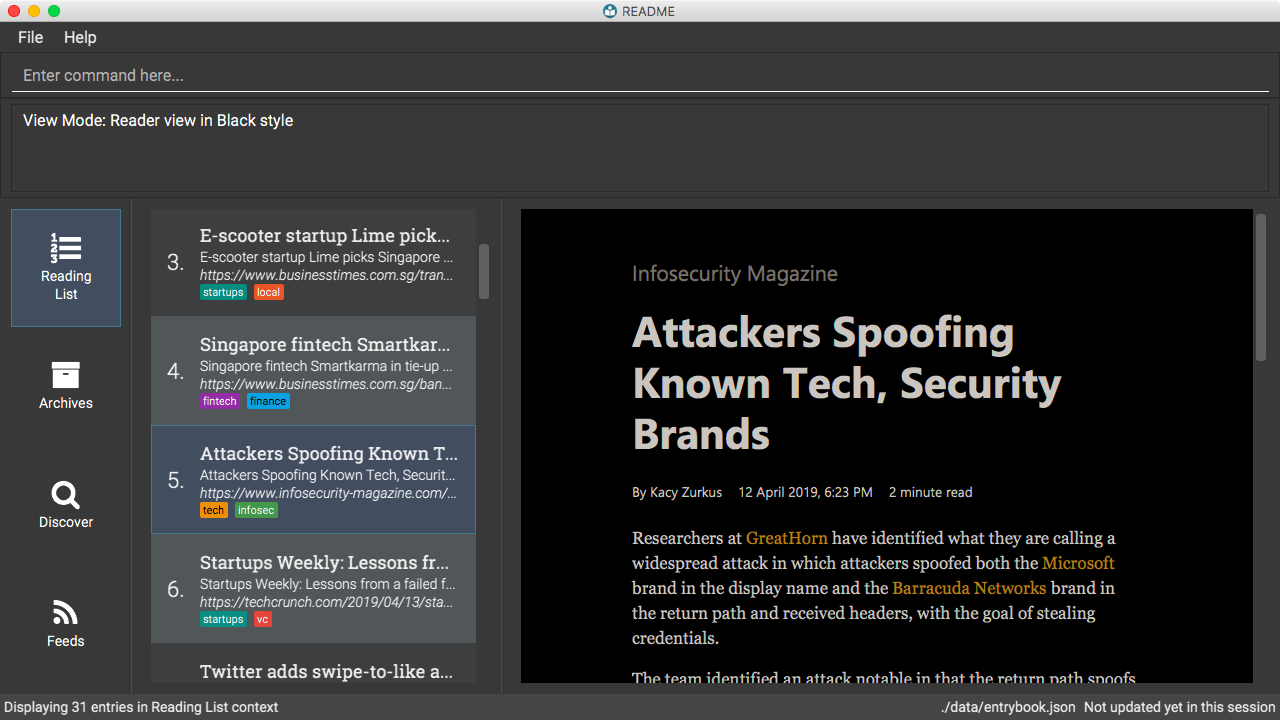
6.4.4. Changing the view mode: view
Changes the view mode between the original browser view or the reader view for a more comfortable reading experience.
Format: view MODE(browser, reader) [s/STYLE(default, sepia, dark, black)]
Examples:
-
Switch to the browser view mode, which displays web pages as they would appear in a web browser.
-
view browser
-
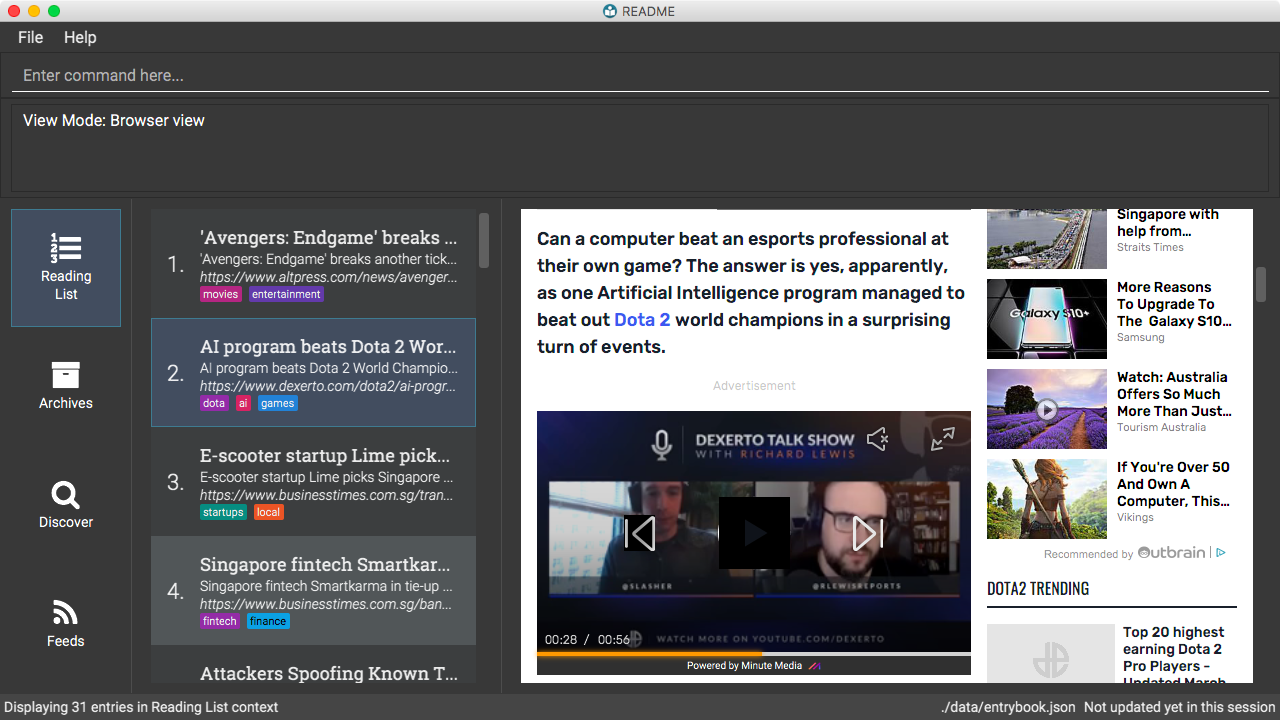
-
Switch to the reader view mode, which strips away clutter and presents content in a clean layout.
-
view reader
-
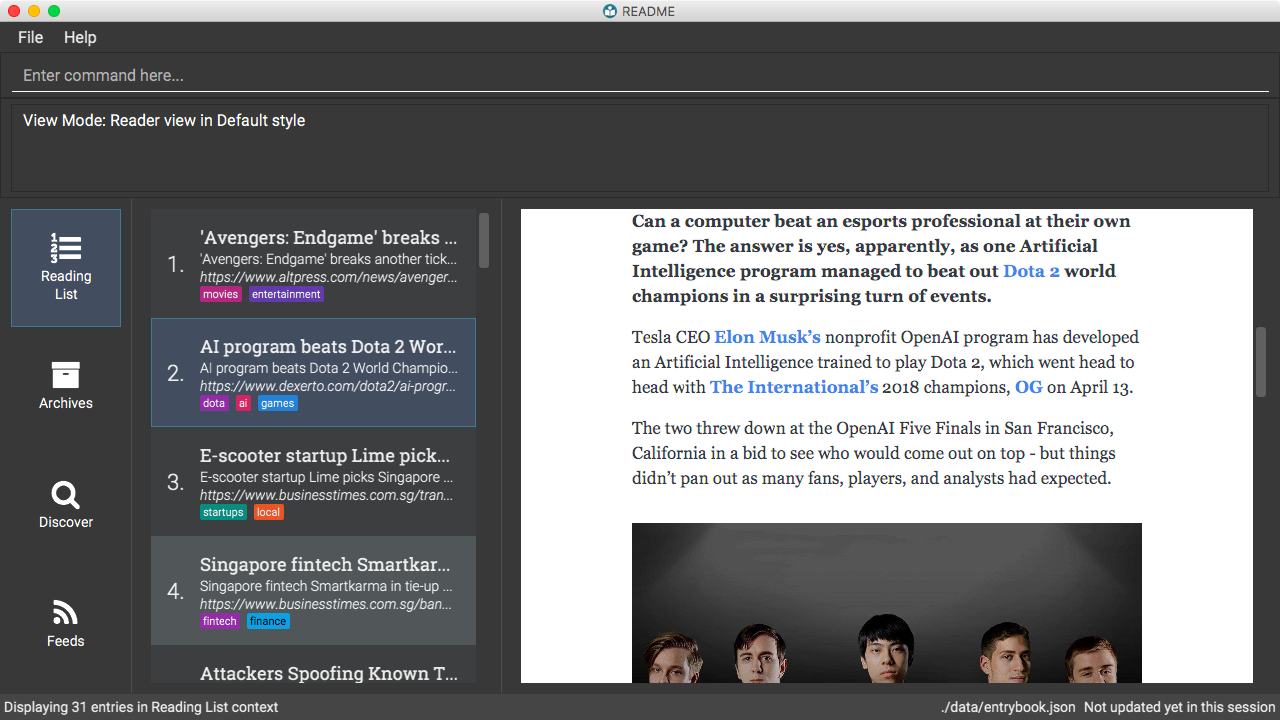
-
Switch to the reader view mode with sepia colour scheme
-
view reader s/sepia
-
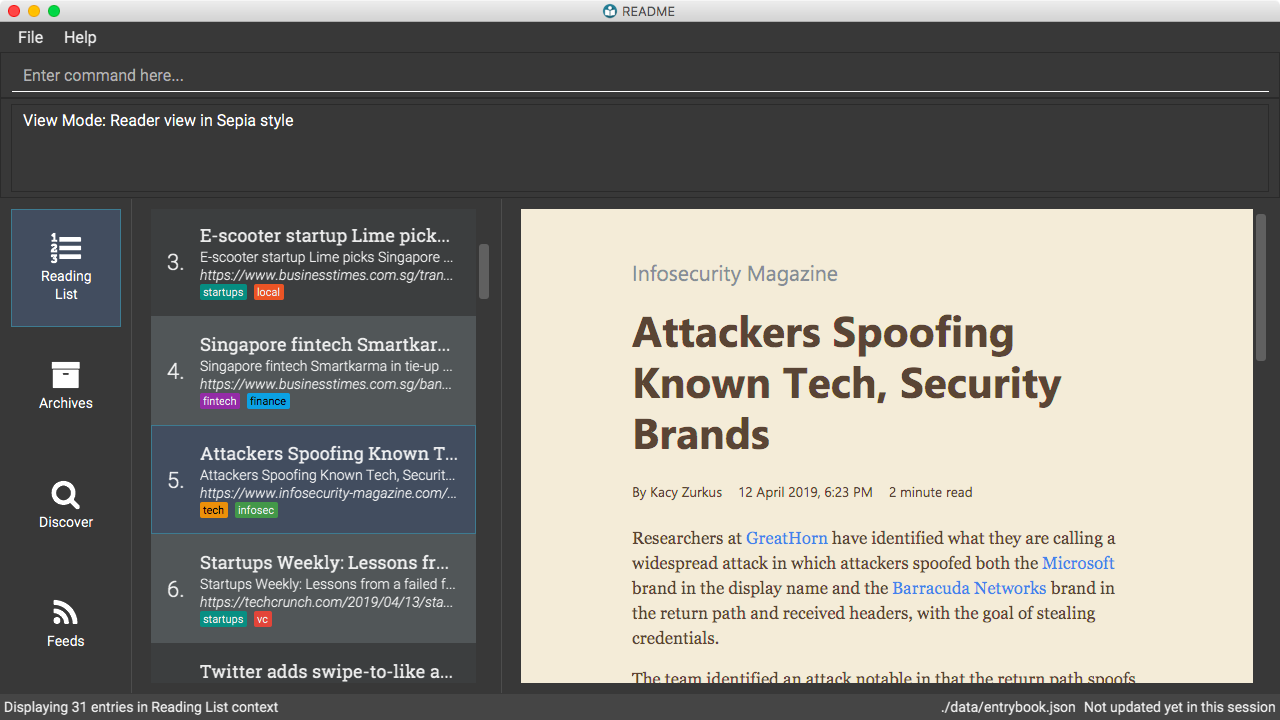
-
Switch to the reader view mode with dark colour scheme
-
view reader s/dark
-
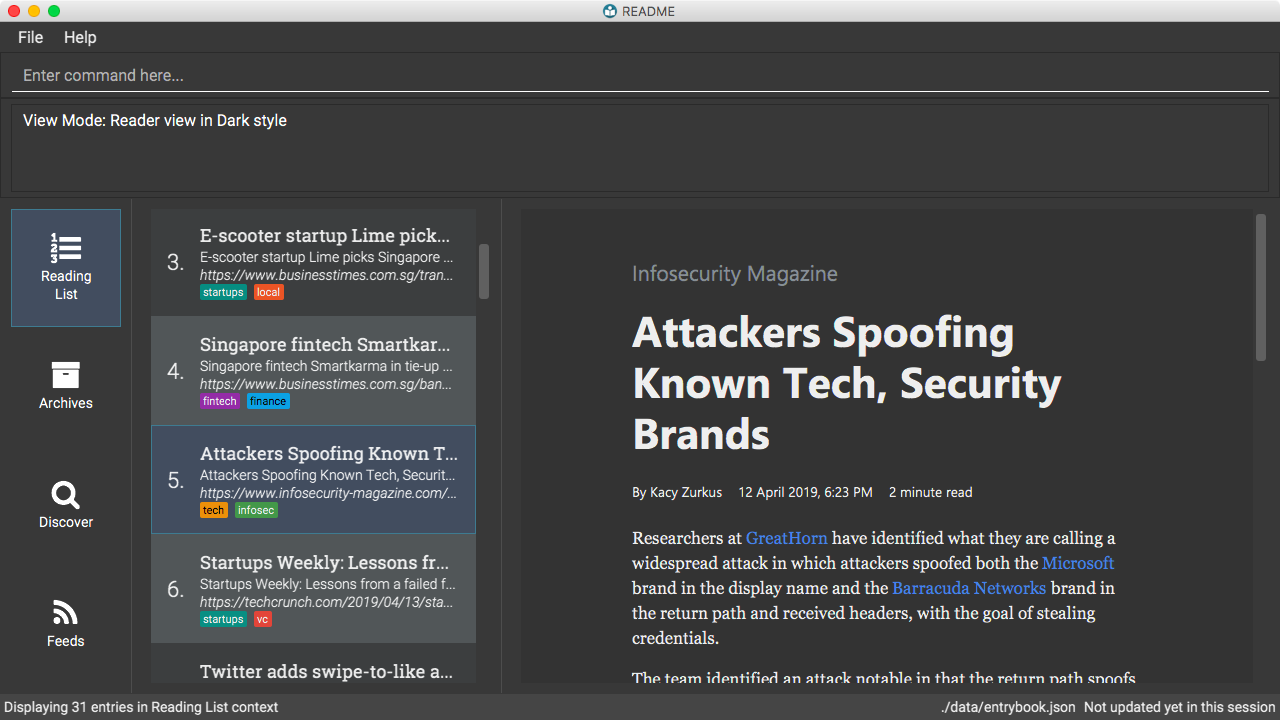
-
Switch to the reader view mode with black colour scheme
-
view reader s/black
-
6.4.5. Refreshing an entry: refresh
If you added an entry a long time ago and you think that the saved page might be outdated,
you can fetch the most updated version from the internet by using this command.
This is helpful for pages such as Wikipedia, which may change often!
See the refreshall command which may be useful to use if you need to refresh a large number of entries at the same time.
Format: refresh INDEX
Examples:
-
Refresh the content of the 2nd entry in the reading list.
-
list -
refresh 2
-
6.4.6. Refreshing all displayed entries: refreshall
Refreshes all currently displayed entries.
Format: refreshall
|
The application may be unresponsive for a short while when refreshing a large number of entries. |
|
You may refer to the |
Examples:
-
Refresh all entries in the reading list. (Will take a long time if you have a large reading list!)
-
list -
refreshall
-
-
Refresh all entries tagged “infoTheory”
-
list -
find t/infoTheory -
refreshall -
list
-
6.4.7. Marking an entry as read: read [coming in v2.0]
Marks the specified entry as read.
Format: read INDEX
Examples:
-
Mark the 2nd entry in the reading list as read.
-
list -
read 2
-
6.4.8. Marking an entry as unread: unread [coming in v2.0]
Marks the specified entry as unread.
Format: unread INDEX
Examples:
-
Mark the 2nd entry in the reading list as unread.
-
list -
unread 2
-
6.4.9. Sharing an entry: share [coming in v2.0]
Shares the specified entry through connected social media.
Format: share INDEX
6.4.10. Archiving an entry: archive
Moves the specified entry to the archive and removes its downloaded content.
Format: archive INDEX
Examples:
-
Move the 2nd entry in the reading list to the archives and remove its downloaded content.
-
list -
archive 2 -
archives
-
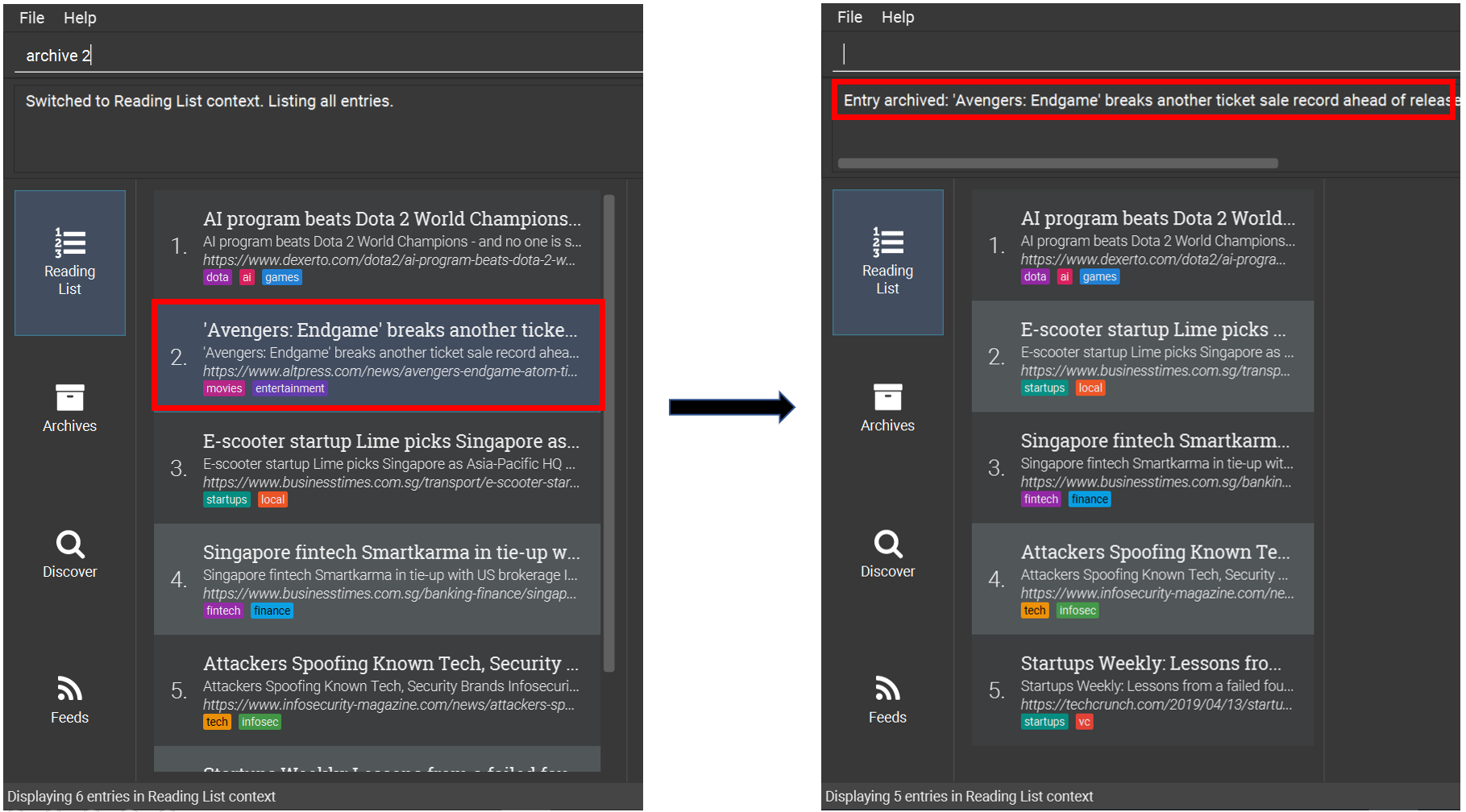
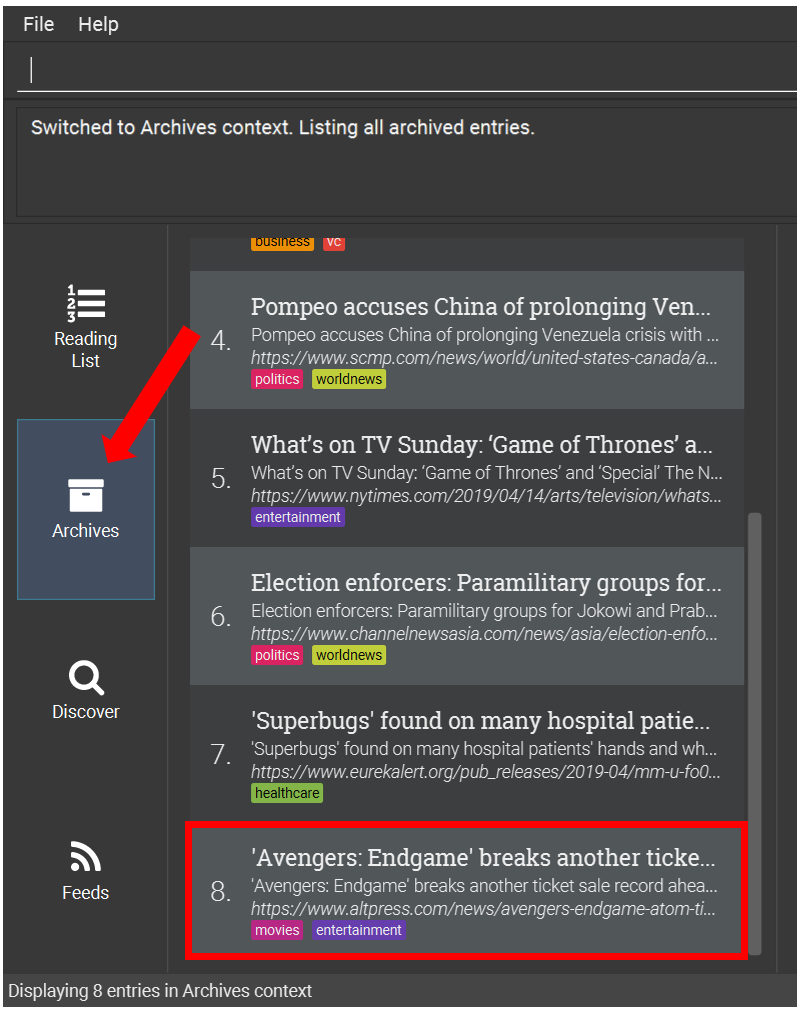
6.4.11. Archiving all displayed entries: archiveall
If you want to archive many entries at the same time,
you can make use of this command to move all the currently displayed entries to the archive,
removing all entries' downloaded content at the same time.
By using a find command first before executing archiveall,
you can archive parts of your reading list by a search criteria.
Format: archiveall
Examples:
-
Archive all entries in the reading list
-
list -
archiveall
-
-
Archive all entries tagged “infoTheory” (you may refer to the figures below)
-
list -
find t/infoTheory -
archiveall -
list
-
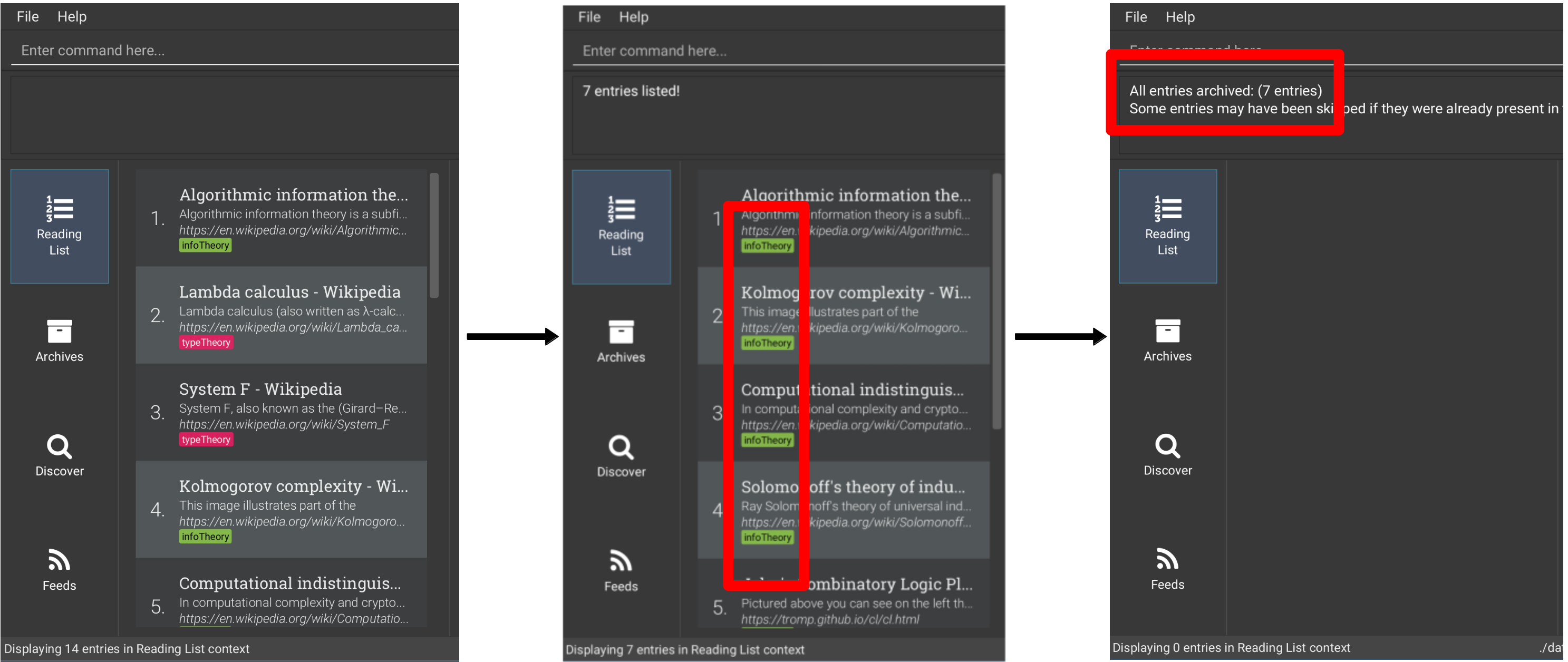
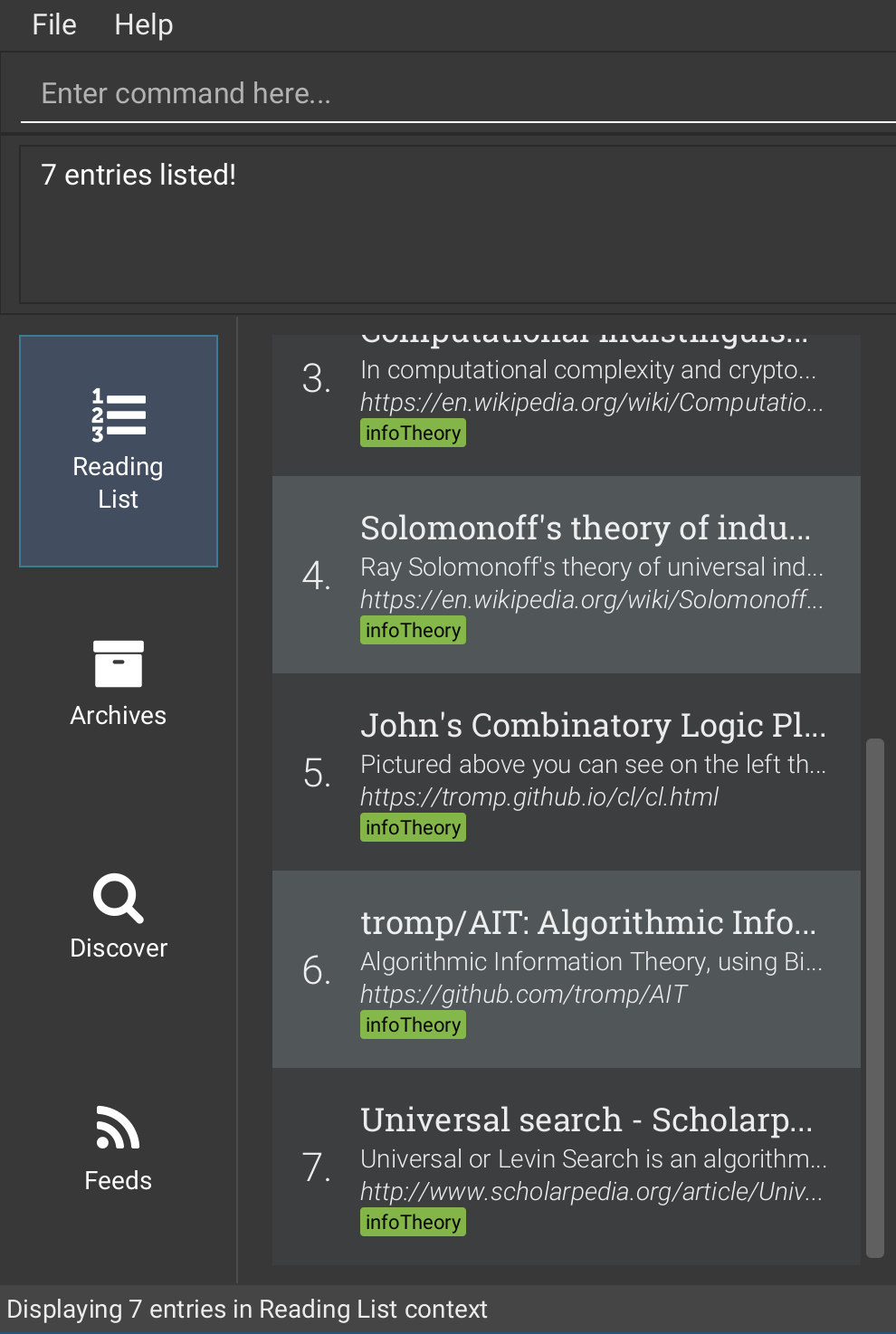
6.4.12. Deleting an entry: delete
Deletes the specified entry from the reading list and removes its downloaded content.
Format: delete INDEX
Examples:
-
Delete the 2nd entry in the reading list.
-
list -
delete 2
-
-
Delete the 1st entry in the results of the
findcommand.-
find Trump -
delete 1
-
6.4.13. Deleting all displayed entries: deleteall
Deletes all currently displayed entries from the reading list, and removes the entries' downloaded content.
Format: deleteall
|
This operation is IRREVERSIBLE! Please take care not to accidentally delete entries you may wish to keep. |
|
You may refer to the |
Examples:
-
Delete all entries in the reading list.
-
list -
deleteall
-
-
Delete all entries whose titles contain “Trump”.
-
list -
find ti/Trump -
deleteall
-
6.5. Archives Context Commands
6.5.1. Finding entries by title: find
Finds entries whose fields contain any of the given keyphrases.
This command behaves the same as the Reading List context find command equivalent.
Format: find [a/SEARCH_PHRASE] [ti/TITLE_SEARCH_PHRASE] [d/DESCRIPTION_SEARCH_PHRASE] [l/LINK_SEARCH_PHRASE] [t/TAG_TO_SEARCH]…
Refer to Section 6.4.2, “Finding entries (by title, description, etc.): find” for examples!
6.5.2. Selecting an entry: select
Selects the entry identified by the index number used in the displayed entry list for reading.
Format: select INDEX
Examples:
Select the 2nd archived entry.
. archives
. select 2
6.5.3. Unarchiving an entry: unarchive [since v1.3]
Moves the specified entry from the archives to the reading list.
Format: unarchive INDEX
Examples:
-
Move the 2nd entry in the archives to the reading list and download its webpage content.
-
archives -
unarchive 2 -
list
-
6.5.4. Deleting an entry: delete
Deletes the specified entry from the archives.
Format: delete INDEX
Examples:
-
Delete the 2nd entry in the archives.
-
archives -
delete 2
-
6.5.5. Deleting all displayed entries: deleteall
Deletes all currently displayed entries from the archives.
Format: deleteall
|
This operation is IRREVERSIBLE! Please take care not to accidentally delete entries you may wish to keep. |
|
You may refer to the |
Examples:
-
Delete all entries in the reading list.
-
list -
deleteall
-
-
Delete all entries whose titles contain “Trump”.
-
list -
find ti/Trump -
deleteall
-
6.6. Search Results Context Commands
6.6.1. Adding entries: addindex
Adds entries from results to the reading list. Content is automatically downloaded to disk.
Format: addindex INDEX
Format: addindex INDEX [ti/TITLE_OVERRIDE] [d/DESCRIPTION_OVERRIDE] [t/TAG]… [coming in v2.0]
Examples:
-
Add the 3rd entry
-
addindex 3
-
-
Add the 1st entry with a description and tagged with “Business”
[coming in v2.0]-
addindex 1 d/explains why UX is important t/Business
-
6.6.2. Adding all displayed entries: addall
Adds all currently displayed entries from results to the reading list. Content is automatically downloaded to disk.
Format: addall
|
The application may be unresponsive for a short while when adding entries from a large search result. |
|
You may refer to the |
Examples:
-
Add all entries that result from searching "Lambda Calculus" on bing.
-
bing Lambda Calculus -
addall
-
-
Add all entries that result from searching "Lambda Calculus" on bing, but only those with a .org domain.
-
bing Lambda Calculus -
find l/.org -
addall
-
6.6.3. Selecting an entry: select
Selects the entry identified by the index number used in the displayed entry list for viewing.
Format: select INDEX
Examples:
-
Selects the 2nd entry from the search results.
-
select 2
-
6.6.4. Changing the view mode: view
Changes the view mode between the original browser or a more comfortable reading experience.
Format: view MODE(browser, reader) [s/STYLE(default, sepia, dark, black)]
Examples:
-
Switch to browser view mode.
-
view browser
-
-
Switch to a clean and clutter-free reader view mode for a more comfortable reading experience.
-
view reader
-
-
Switch to reader view mode with dark style colour scheme.
-
view reader s/dark
-
6.7. Feeds Context Commands
6.7.1. Updating entries from feeds: refresh
Refreshes a feed.
Format: refresh INDEX
Format: refesh all [coming in v2.0]
Examples:
-
Update entries from all feeds.
[coming in v2.0]-
refresh all
-
-
Update entries from the 2nd feed.
-
refresh 2
-
|
The application may be unresponsive for a short while when adding entries from a large feed. |
6.7.2. Updating entries from all currently displayed feeds: refreshall
Refreshes all currently displayed feeds.
Format: refreshall
|
The application may be unresponsive for a short while when adding entries from a large feed, or when refreshing many feeds. |
|
You may refer to the |
Examples:
-
Refresh all subscribed feeds
-
feeds -
refreshall
-
-
Refresh all news feeds
-
feeds -
find ti/News -
refreshall
-
6.7.3. Selecting a feed: select
Selects the feed identified by the index number used in the displayed feed list and displays its entries.
Format: select INDEX
Examples:
-
Select the 2nd feed in the manager and displays its entries.
-
select 2
-
6.7.4. Editing a feed: edit [coming in v2.0]
Edits an existing feed in the manager.
Format: edit INDEX [u/URL] [n/NAME] [t/TAG]…
Examples:
-
Edit the name of the 1st feed.
-
edit 1 n/HackerNews
-
-
Clear all existing tags from the 2nd feed.
-
edit 2 t/
-
6.7.5. Unsubscribing from a feed: unsubscribe
Deletes the specified feeds from the manager and unsubscribes from them, but existing entries obtained from that feed will not be deleted.
Format: unsubscribe INDEX
Examples:
-
Delete the 2nd shown feed.
-
unsubscribe 2
-
6.7.6. Clearing all feeds : clear [coming in v2.0]
Clears all followed feeds from the manager.
Format: clear
6.8. Feeds Search Context Commands [coming in v2.0]
6.8.1. Subscribing to a feed: subscribe
Adds a feed from the search results to the manager and subscribes to updates.
Format: subscribe INDEX [n/NAME] [t/TAG]…
Format: subscribe INDICES [t/TAG]…
Format: subscribe all
|
A feed can have any number of tags (including 0) |
Examples:
-
Add all shown feeds.
-
subscribeall
-
-
Add a feed whose name is “Engadget” and whose entries will be tagged with
Tech.-
subscribe 1 n/Engadget t/Tech
-
-
Add the 5th to 9th feeds whose entries will be tagged with
Work.-
subscribe 5-9 t/Work
-
6.8.2. Selecting a feed: select
Selects the feed identified by the index number used in the displayed feed list.
Format: select INDEX
Examples:
-
Selects the 2nd feed from the feeds list.
-
select 2
-
7. FAQ
Q: Why is reader view not displaying any buttons or input fields?
A: Reader view only keeps text content and is not meant to used for web forms.
Q: Why is reader view not working?
A: We cannot guarantee Reader view works on every website.
8. Command Summary
8.1. Anywhere
| Command | Summary |
|---|---|
|
Adds a single entry. |
|
Subscribes to a single feed. |
|
Lists all commands entered previously in reverse order. |
|
Enables or disables internet connectivity. |
|
Opens the User Guide in a new window. |
|
Exits the application. |
8.2. Reading List Context
| Command | Summary |
|---|---|
|
Switches to list context. |
|
Edits the entry specified by the index. |
|
Finds entries matching the given arguments. |
|
Selects the entry specified by the index for viewing. |
|
Re-downloads the webpage content of the entry specified by the index. |
|
Re-downloads the webpage content of the entry specified by the index. |
|
Archives the entry specified by the index. |
|
Archives all displayed entries. |
|
Deletes the entry specified by the index. |
|
Deletes all displayed entries. |
|
Deletes all entries. |
|
Changes the view mode of the browser panel. |
8.3. Archives Context
| Command | Summary |
|---|---|
|
Switches to archives context. |
|
Finds entries matching the given arguments. |
|
Selects the entry specified by the index for viewing. |
|
Unarchives the entry specified by the index, adding it back to the reading list. |
|
Unarchives all displayed entries, adding them back to the reading list. |
|
Deletes the entry specified by the index. |
|
Deletes all displayed entries. |
|
Deletes all entries. |
8.4. Search Result Context
| Command | Summary |
|---|---|
|
Searches Bing for entries that you can subsequently add. |
|
Searches Google News for entries that you can subsequently add. |
|
Opens a web feed at the URL for previewing. |
|
Adds the entry specified by the index to the reading list. |
|
Adds all displayed entries to the reading list. |
|
Selects the entry specified by the index for viewing. |
|
Changes the view mode of the browser panel. |
8.5. Feeds Context
| Command | Summary |
|---|---|
|
Switches to feeds context. |
|
Refreshes the feed specified by the index. |
|
Refreshes all feeds. |
|
Selects the entry specified by the index for viewing. |
|
Unsubscribes and deletes the feed specified by the index. |